The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a global exemplar of technological and scientific advancement, particularly in the realm of biomedical research. Originating during pivotal moments such as World War II, this partnership between government entities, academic institutions, and private industry has propelled groundbreaking medical breakthroughs, notably the mass production of penicillin. Historical research funding has been critical, ensuring continuous investment in public-private collaborations that advance healthcare solutions. As scrutiny over federal funding rises, this intricate system faces challenges that could impact the momentum of medical development. However, the resilience of the U.S. innovation ecosystem reflects its foundational role in shaping not just American science but global health trends.
The landscape of American ingenuity encompasses a vast network of collaborative efforts that fuel advancements in various sectors, with a notable emphasis on health and technology. This thriving environment, characterized by synergy between public institutions and private enterprises, has been vital for fostering innovations such as life-saving drugs and novel therapies. The legacy of World War II science illustrates how strategic research initiatives birthed a robust biomedical sector, setting standards for future efforts. By understanding the dynamics of historical research funding and its implications on today’s projects, we can better appreciate the sustained progress in medical solutions and the importance of nurturing these partnerships moving forward. As the world grapples with emerging health challenges, the need for a well-functioning innovation system remains more critical than ever.
The Historical Roots of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has its roots deeply embedded in the urgent demands of World War II. A significant turning point occurred in June 1940 when a collective of visionary leaders from U.S. universities and industrial research labs presented a bold proposal to President Franklin D. Roosevelt. This initiative aimed to leverage civilian scientists to develop pivotal technologies for the military, which at that time was grappling with technological deficiencies. This early collaboration was not only about meeting wartime needs but also laid the groundwork for a system that would evolve into a powerhouse for biomedical research and innovation, marking a profound shift in how the government, academia, and private industry interacted and collaborated.
The cooperation established during World War II propelled forward advancements across various scientific fields, particularly in biomedicine. The establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) played a crucial role in coordinating wartime research efforts, leading to monumental breakthroughs in medical technology. This era spurred unprecedented growth in research funding and scientific inquiry that extended well beyond the war, fostering an environment conducive to public-private partnerships that would define the innovation ecosystem of the U.S. for generations. As we reflect on these historical milestones, it’s clear that this collaboration not only supported the war effort but became a cornerstone for ongoing medical breakthroughs and public health advancements.
Public-Private Partnerships: The Heart of Innovation
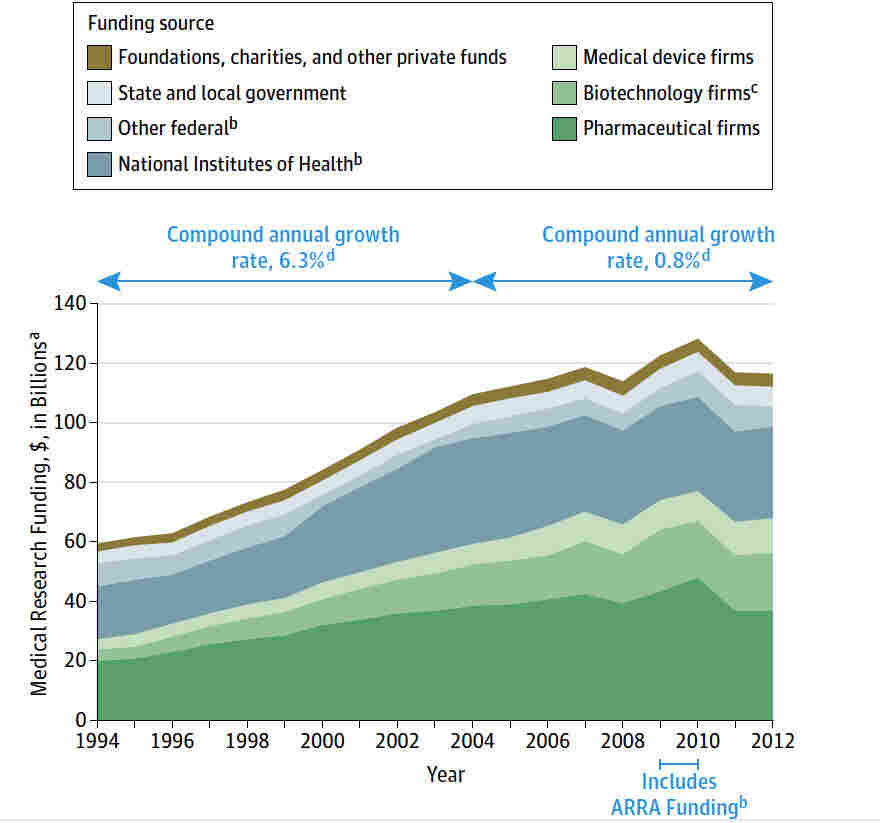
Public-private partnerships have historically served as the backbone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the realm of biomedical research. Through shared resources and collaborative goals, such partnerships have enabled the rapid advancement of medical breakthroughs and technologies that have profoundly impacted public health. The government’s investment in research through entities like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has shown how strategic funding can ignite innovation, improve healthcare outcomes, and stimulate economic growth. The results of these partnerships are evident in the numerous drugs and therapies developed as a direct result of federal and private collaboration.
In the context of rising concerns regarding federal funding cuts, particularly affecting biomedical science, the value of these partnerships becomes even more pronounced. As debates surrounding reimbursement for indirect research costs intensify, it’s essential to recognize the long-term stability and growth fostered by public-private initiatives. The legacy of World War II not only influenced immediate wartime needs but set a blueprint for ongoing collaboration that has led to continuous advancements in healthcare technology and disease treatment, continually reminding us of the innovative spirit and resilience inherent in these partnerships.
The Impact of World War II on Biomedical Research
World War II served as a catalyst for significant advancements in biomedical research that have shaped the landscape of health science as we know it today. The urgency of military needs prompted a rapid acceleration in research capabilities, leading to the creation of groundbreaking medical technologies and treatments. Notably, the development and mass production of penicillin, facilitated by the OSRD, demonstrated how targeted research funding could yield transformative results, saving countless lives both during and after the war. This breakthrough illustrated the necessity of scientific innovation in addressing wartime health crises and laid the groundwork for the expansion of antibiotic development that would follow.
Moreover, the lessons learned during World War II instilled a sense of urgency and organized effort towards combating infectious diseases, which have historically posed significant threats to both military and civilian populations. Through strategic coordination among universities, government agencies, and the pharmaceutical industry, the groundwork was laid for a robust public-private partnership model that continues to drive biomedical research today. The historical context of this collaboration underscores not only the success achieved during times of crisis but also the ongoing need for this synergistic approach to address contemporary health challenges.
Lessons from the Postwar Era: Building a Better Future
The postwar period following World War II provided a unique opportunity to build upon the research and development successes achieved during the conflict. The foundation established through wartime collaborations between the federal government, universities, and private industry catalyzed a golden age of biomedical research. New scientific understandings, innovative drug development platforms, and enhanced training for the next generation of scientists emerged from this period. As the lessons from the war were integrated into academic and industry practices, the U.S. became a world leader in health innovation, charting a course for unparalleled advancements in medical care and treatment.
As we reflect on the success of the public-private partnerships initiated during and after World War II, it’s crucial to consider how these lessons can be applied to address contemporary and future challenges in biomedical research. The ongoing investment in developing human capital—training thousands of scientists and emerging researchers—was a critical outcome of wartime efforts. Today, as we navigate a landscape of changing funding dynamics and the importance of maintaining the integrity of research processes, the historical successes of public-private partnerships serve as a valuable blueprint for fostering innovation and ensuring the continued advancement of health science.
Challenges and Controversies in Current Research Funding
As the environment around research funding evolves, the U.S. innovation ecosystem faces new challenges and controversies. Recent debates over capping reimbursement for indirect research costs raise significant concerns about the sustainability of public funding for biomedical research. Critics argue that such measures could undermine the foundation of public-private partnerships that have been instrumental in catalyzing advancements in healthcare. The potential withdrawal of resources from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) could adversely affect the intricate web of collaboration that supports not only research but also the training of future scientists who will shape the next era of medical breakthroughs.
The scrutiny of federal financial support for research invites broader questions about the efficacy and efficiency of current funding mechanisms. Emphasizing the need for balanced funding that recognizes both the immediate costs of research and the long-term benefits of investment can help maintain the momentum of innovation established in the postwar era. Protecting the golden goose of the U.S. biomedical innovation system is imperative, as the partnership model has been credited with significant advances in medical technology and public health. Setting the right policies to encourage and sustain these partnerships is crucial in ensuring the continued success of the nation’s health sector.
The Role of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) plays a pivotal role in the U.S. innovation ecosystem, serving as a key funder of biomedical research that drives medical advancements and technological innovation. Established to support medical research and ensure the nation remains at the forefront of health innovation, the NIH has been foundational in fostering collaboration between academia, private sector firms, and government entities. The sustained investment into research and development by the NIH has led to significant medical breakthroughs, shaping the landscape of treatments and therapies available today, from cancer treatments to chronic disease management.
Furthermore, the NIH’s influence extends beyond funding; it also sets high standards for research quality and integrity, promoting best practices across the biomedical community. The impact of NIH-funded research can be observed not only in the advancements it directly supports but also in how it stimulates economic growth through job creation in research institutions and related industries. As we see shifts in governmental support for research funding, the importance of the NIH as a stabilizing force within the public-private partnership model cannot be overstated. Protecting and enhancing its capacity to support biomedical innovation is crucial for the future of health advancements in the U.S. and beyond.
Innovations in Drug Development: A Continuous Journey
Innovations in drug development have been significantly shaped by the ongoing collaboration between federal agencies, private sector companies, and academic institutions. The advancements achieved during World War II, particularly through programs like the OSRD, established a precedent for future collaborations that focus on tackling pressing healthcare challenges. The success of penicillin development and subsequent antibiotic discoveries can be traced back to these initial efforts, which provided the framework for systematic research methodologies and regulatory processes that guide today’s drug approval system. This evolutionary journey highlights the importance of collaborative efforts in addressing the complex challenges of drug discovery.
As the scientific field progresses, it continues to embrace new technologies and methodologies that enhance drug development capabilities. Current trends in personalized medicine, biotechnology, and digital health are examples of how researchers are leveraging sophisticated tools and data analytics to create targeted therapies. The U.S. innovation ecosystem has become a testing ground for these cutting-edge advances, driven by the historical legacy of public-private partnerships formed during critical moments of need, such as World War II. Understanding this historical context is vital for fostering an environment where future breakthroughs can flourish, ensuring that the momentum gained from the past informs future health innovations.
Training the Next Generation of Scientists
One of the less emphasized yet critical outcomes of the innovation ecosystem established during World War II is the training and development of the next generation of scientists. Engaging thousands of graduate students, young researchers, and new Ph.D. graduates in the war effort not only contributed to immediate research needs but also established a well-prepared workforce for future challenges in biomedical research. This opportunity for hands-on experience in real-world scientific exploration enriched their training and became instrumental in forming a knowledgeable base that would sustain ongoing advancements in health science research.
Today, the legacy of that era continues to influence educational priorities within the scientific community. Programs aimed at mentoring and involving students in cutting-edge research provide invaluable opportunities that not only enhance their skills but also help foster a culture of innovation. As new technologies and scientific methodologies emerge, maintaining a focus on developing human capital is essential. Ensuring that future researchers are equipped to navigate and contribute to the complex fields of biomedical research will be vital for continuing the positive trajectory of innovation that has characterized the U.S. health ecosystem.
The Future of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
Looking ahead, the future of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedicine, appears to be poised for continued growth and transformation. While historical successes have laid a strong foundation, it is essential to adapt and evolve in response to modern challenges and opportunities. The rise of personalized medicine, genomics, and digital health technologies presents new frontiers for exploration, necessitating innovative approaches and collaboration among public and private sectors. The commitment to sustaining and enhancing research funding will play a crucial role in harnessing these advancements to improve healthcare outcomes.
Additionally, ensuring robust public-private partnerships that promote continuous feedback and collaboration among scientists, companies, and government agencies will be key to navigating the complexities of emerging scientific questions. The ongoing discourse surrounding federal research funding highlights the need to protect and nurture the existing ecosystem that has yielded remarkable medical advancements. As we stand at the intersection of past achievements and future possibilities, it is imperative to remain vigilant and proactive in preserving the innovative spirit that has characterized the U.S. innovation ecosystem for the last 80 years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of the U.S. innovation ecosystem on biomedical research?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem significantly impacts biomedical research by providing a robust framework for public-private partnerships. This collaboration fosters groundbreaking medical breakthroughs, as seen during World War II when federal funding and scientific innovation led to the mass production of penicillin. Such partnerships continue to enhance research capabilities, driving advancements in health and technology.
How did historical research funding shape the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Historical research funding has been central to shaping the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the biomedical sector. The establishment of funding mechanisms during World War II laid the groundwork for ongoing collaborations between the government, academic institutions, and private industry. This model has fostered significant medical breakthroughs and a thriving environment for scientific discovery.
What role did public-private partnerships play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem during World War II?
Public-private partnerships were crucial in the U.S. innovation ecosystem during World War II, driving rapid advancements in technology and medicine. These partnerships enabled the coordination of resources and expertise, leading to significant innovations like penicillin production. The successful collaboration established a precedent that continues to influence biomedical research and development today.
Why is the U.S. innovation ecosystem considered the envy of the world?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is often considered the envy of the world due to its successful integration of academic research, government funding, and industrial development. This unique collaboration has resulted in numerous medical breakthroughs and technological advancements, positioning the U.S. as a leader in science and innovation.
What historical events contributed to the development of the U.S. biomedical innovation system?
The development of the U.S. biomedical innovation system is heavily rooted in historical events like World War II. The urgent need for medical solutions during the war prompted significant government funding and organized research efforts, leading to advancements in drug development and infectious disease control. This foundation has supported continuous growth and innovation in the biomedical field.
How do government policies influence the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Government policies influence the U.S. innovation ecosystem by providing essential funding and creating frameworks for collaboration among academia, industry, and federal agencies. Policies that promote public-private partnerships and support research funding lead to enhanced biomedical research outcomes and pioneering medical breakthroughs, ensuring the system remains effective and innovative.
What are the challenges facing the U.S. innovation ecosystem today?
Today, challenges facing the U.S. innovation ecosystem include potential funding cuts to federal research programs like the National Institutes of Health. Questions surrounding the reimbursement for indirect research costs also pose concerns for biomedical researchers. Addressing these challenges is crucial to maintaining the ecosystem’s success and fostering continued innovation.
In what ways did World War II transform the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
World War II transformed the U.S. innovation ecosystem by establishing a collaborative environment among the federal government, industry, and research institutions. The war necessitated urgent technological advancements, leading to significant funding for biomedical research and the development of new drug production methods. This collaboration laid the foundation for ongoing innovations in medicine and technology.
What lessons can be learned from the U.S. innovation ecosystem’s history for future biomedical research?
The history of the U.S. innovation ecosystem teaches valuable lessons for future biomedical research, particularly the importance of sustained funding, collaboration between public and private sectors, and the need for a supportive infrastructure. The successful model established during World War II demonstrates that strategic partnerships and investments in research can yield significant health advancements and innovations.
How has the collaboration between universities and the federal government evolved in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The collaboration between universities and the federal government in the U.S. innovation ecosystem has evolved significantly over the past 80 years. Initially, this partnership was focused on wartime needs, but it has grown to encompass a wide array of research areas. Today, this collaboration underpins much of the biomedical research landscape, driving breakthroughs and strengthening the overall innovation system.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Historical Context | The U.S. innovation ecosystem in health originated during World War II, utilizing government-supported research to develop vital technologies. |
| Government Participation | Federal funding has greatly supported innovation in medicine, technology, and many fields, especially via partnerships with academia. |
| Impact of Penicillin Development | Mass production of penicillin transformed military and civilian healthcare, reducing diseases that affected soldiers by up to 100%. |
| Research Infrastructure | The establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) during WWII marked a significant organizational advancement for R&D. |
| Public-Private Collaboration | The partnership between federal government and private sector has endured since WWII, fostering biomedicine growth. |
| Future of Innovation | Maintaining and supporting this ecosystem is crucial for continued success and innovation in U.S. health and technology. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has become the envy of the world, primarily due to its robust public-private partnerships that date back to World War II. This collaboration has not only proved pivotal in healthcare advancements, such as the mass production of penicillin but has also laid a foundation for ongoing research and development across various sectors. The careful balance of federal funding and private sector ingenuity has consistently propelled the U.S. ahead in technological and biomedical innovations, making it essential to protect and enhance this successful model for future growth.