Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked extensive debate among nutritionists and health professionals alike. While sugar, especially in the form of processed foods, can lead to cravings and compulsive consumption, it doesn’t fit the clinical definition of addiction that applies to substances like alcohol or nicotine. The effects of sugar on our brains can mirror those of addictive substances, arousing strong sugar cravings and leading to habitual sugar consumption. As our diets become increasingly saturated with added sugars, understanding sugar addiction and its associated effects is crucial for our overall health.
Exploring the nature of sugar as a potentially habit-forming substance opens up discussions about sweeteners in our diets. Many people report intense cravings for sugary foods, which can create a cycle of overindulgence similar to that experienced with more widely recognized addictive substances. The relationship between sugar and processed food consumption plays a significant role in these behaviors, leading us to consider how we might manage our intake of these sweeteners. By examining the question, “Is sugar a habit-forming element?”, we shine a light on the broader implications of sugar consumption and its impact on our health.
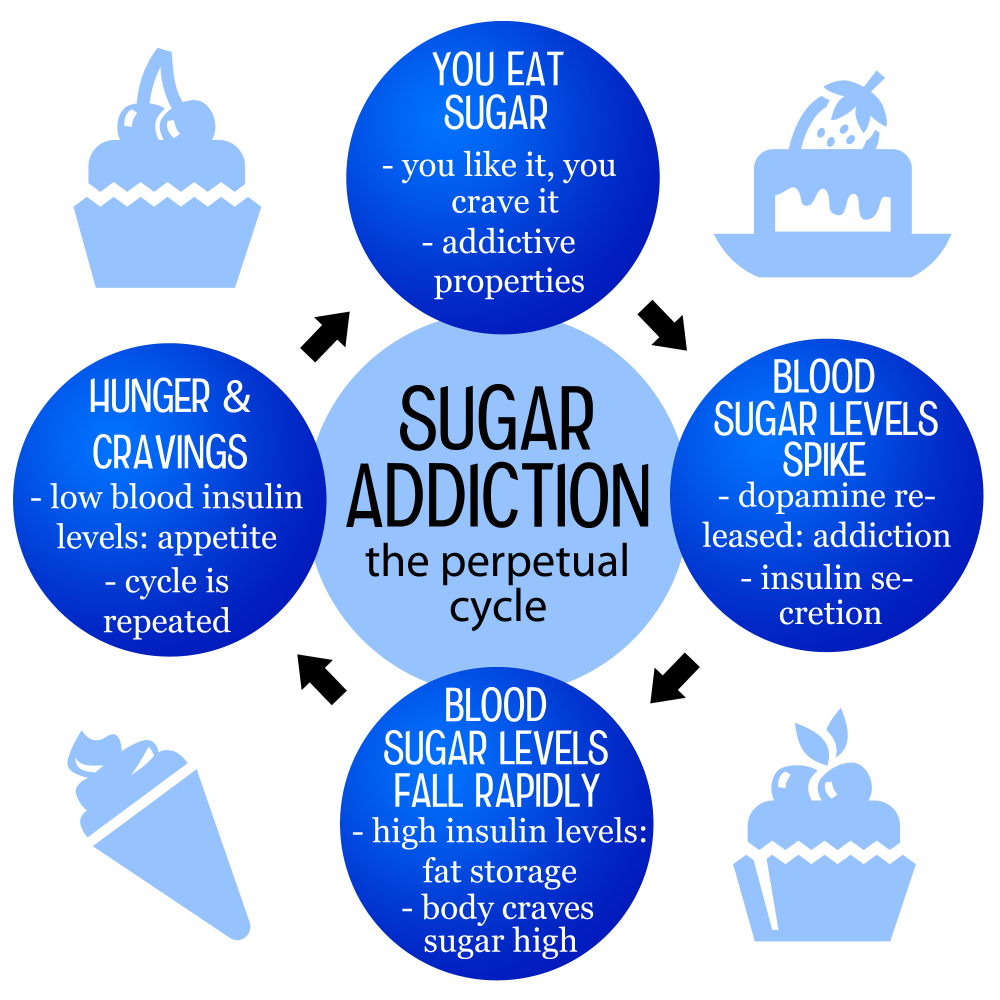
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a complex issue that intertwines both psychological and physiological factors. Many individuals experience intense cravings for sugary foods, often leading to compulsive eating behavior. This can be attributed to sugar’s ability to stimulate the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Our bodies may come to rely on this hit of pleasure, particularly from ultra-processed foods rich in sugar, which can reinforce these cravings over time.
Unlike substances like alcohol and nicotine, sugar is not classified as an addictive drug according to clinical criteria. However, the nature of sugar cravings can lead some to perceive their relationship with sugar in a similar manner. With the prevalence of added sugars in nearly all processed foods, the average American consumes close to 20 teaspoons per day, which significantly exceeds recommended limits. Such high consumption not only supports habitual sugar intake but may also cause withdrawal-like symptoms when attempts are made to cut back.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
The health implications of excessive sugar consumption are well-documented. High sugar intake has been linked to numerous adverse health effects, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Furthermore, consuming high volumes of sugary foods can alter human metabolism and lead to increased fat storage, particularly around the abdomen. The temptation of sugar-laden foods is compounded by their availability and palatability, creating a cycle of desire that can be difficult to break.
Moreover, the physiological effects of sugar go beyond mere calories. Research indicates that excessive sugar can influence mood and energy levels, leading to highs followed by crashes that may contribute to symptoms of anxiety and depression. In the long run, it is essential to monitor one’s sugar intake and opt for healthier alternatives to safeguard physical and mental wellbeing.
Recognizing the effects of sugar consumption can empower individuals to make informed food choices. By paying attention to food labels and gradually reducing added sugars, individuals can break free from these cravings and foster healthier eating habits.
Sugar Cravings: Causes and Solutions
Sugar cravings can often be triggered by both physiological and psychological factors. When individuals consume processed foods high in sugar, their bodies quickly react by craving more due to the spikes and drops in blood sugar levels. Additionally, emotional states, such as stress or boredom, can also lead to increased cravings for sugary snacks, making it vital to understand these triggers to manage them effectively.
To combat sugar cravings, experts recommend a multi-faceted approach. Incorporating whole foods, which are lower in sugar and higher in nutrients, can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings. Additionally, maintaining regular meal patterns that include adequate protein and healthy fats can contribute to sustained energy levels and diminish the desire for quick-sugar fixes.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption
Processed foods are often the primary culprits behind excessive sugar consumption. These foods typically contain added sugars that enhance flavor, extend shelf life, and provide a desirable texture. Unfortunately, the convenience of these processed options often overshadows health concerns, leading to increased intake of added sugars without an understanding of the implications. The challenge lies in the sheer accessibility of these foods, which are marketed heavily and readily available.
To promote better health, it is crucial to limit processed food consumption and instead focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Choosing fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lead to a more balanced diet rich in nutrients while limiting added sugars. By educating ourselves and making conscious choices in our food selections, we can take significant steps towards improving our health and well-being.
Gradual Reduction of Sugar Intake
Many people attempt to eliminate sugar from their diets abruptly, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and mood swings. Instead of going cold turkey, nutritionists recommend a gradual reduction in sugar intake to mitigate these effects. This approach allows the body to adjust while maintaining dietary satisfaction, effectively reducing sugar cravings over time.
Creating a plan for gradual reduction involves clearing sugary snacks from the home and replacing them with healthier options. By incorporating natural sweeteners or fruits, one can satisfy cravings without excessive sugars. Furthermore, keeping a food diary can help individuals track their progress and identify specific eating patterns that may need adjustment through mindfulness and intentional choices.
Mindful Eating Practices
Mindful eating is an effective strategy for managing sugar cravings and promoting healthier eating habits. This practice involves paying close attention to the food one consumes, including its texture, flavor, and origins. By engaging fully with the eating experience, individuals can develop a better understanding of their hunger cues, emotional triggers, and overall relationship with food.
Incorporating mindful eating practices can help lessen cravings as individuals learn to appreciate food more holistically rather than consuming it thoughtlessly. Techniques such as savoring each bite, eating without distractions, and focusing on the meal’s sensory aspects can transform one’s outlook on sugar and processed food, leading to better choices and reduced consumption over time.
Why Sweetness Matters in Our Diet
While sugar is often viewed negatively due to its potential for addiction and health issues, it’s essential to recognize that sweetness holds an important place in our diets. Natural sugars found in fruits and dairy contribute not only to flavor but also to the overall enjoyment of food. A balanced diet can include these natural sugars, providing nutrients and satisfaction while ensuring that sweetness is still a part of a nutritious lifestyle.
Moreover, enjoying sweetness in moderation can enhance psychological well-being. Life’s sweet moments, including indulging in a treat now and then, can contribute to a healthier mindset. Instead of labeling sugar solely as an enemy, fostering a balanced view can empower individuals to indulge responsibly without guilt, leading to more sustainable dietary habits.
The Importance of Reading Food Labels
Being informed about what we consume is crucial in managing sugar intake effectively. Reading food labels can reveal the amount of added sugars present in products, aiding individuals in making healthier choices. Many processed foods contain surprising amounts of sugar, often disguised under various names, making it vital to scrutinize labels to understand one’s sugar consumption.
Moreover, educating oneself on food labeling can increase awareness of overall dietary habits. By recognizing hidden sugars in favorite foods and snacks, individuals can make informed choices that align better with their health goals. It’s an empowering act that can lead to more conscientious consumption and ultimately contribute to better health outcomes.
Community and Support in Reducing Sugar Intake
Tackling sugar cravings and managing intake can feel isolating, but community support can make a significant difference. Whether joining a local health group or finding friends and family willing to participate in healthier eating challenges, sharing experiences can foster motivation and accountability. Community resources, such as workshops or discussions led by nutritionists, can enhance understanding and provide practical tools for reducing sugar consumption.
In addition, engaging with supportive communities can help individuals feel less alone in their health journeys. Success stories, challenges, and strategies shared within these environments can empower individuals to sustain their efforts in reducing sugar intake. Ultimately, connection fosters resilience and commitment to healthier choices, demonstrating that collective efforts can lead to profound changes in dietary habits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar does enhance cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as addictive in the same way that drugs or alcohol are. The physiological and psychological effects of sugar consumption are real, but they do not match the clinical addiction criteria set for substances like nicotine or opiates.
What are the effects of sugar on the body?
High sugar consumption can lead to numerous negative health effects, including obesity, increased risk of heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Additionally, sugar can cause spikes and crashes in blood glucose levels, leading to cravings for more sugary foods and compulsive eating, similar to addictive substances.
How do sugar cravings compare to cravings for addictive substances?
Sugar cravings can resemble cravings for addictive substances in that they may trigger withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced suddenly. However, the severity of these symptoms is significantly milder than those produced by addictions to alcohol or drugs. Understanding the impact of processed foods, which are high in added sugars, is critical in discussing sugar consumption.
Can cutting out sugar completely lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, abruptly eliminating sugar can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. This is especially true for individuals who consume large amounts of sugar through processed foods. A gradual reduction in sugar consumption is recommended to minimize such effects.
Is all sugar the same when it comes to addiction?
No, not all sugar has the same effects. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are part of a balanced diet and are necessary for health. In contrast, added sugars found in processed foods are linked to negative health outcomes and may contribute to cravings and habits associated with sugar addiction.
What recommendations exist for sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children. Being mindful of labels and the sugar content in processed foods is key to managing sugar intake effectively.
How can one manage sugar cravings healthily?
Managing sugar cravings can be achieved through gradual reduction of added sugars, increasing fiber intake, and choosing whole foods over processed options. Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate sleep can also play a role in minimizing sugar cravings and promoting healthier eating habits.
Are processed foods a major source of sugar addiction?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can enhance their palatability and lead to habitual consumption. Being aware of these ingredients can help individuals make healthier food choices and potentially reduce cravings related to sugar addiction.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Classification of Sugar | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, despite its ability to create cravings. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Eating high amounts of sugar can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when stopped, such as headaches and anxiety. |
| Nutrition Recommendations | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake: 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women. |
| Understanding Consumption Habits | Most people in the U.S. consume nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, often from processed foods. |
| Gradual Reduction | Avoid going cold turkey on sugar; it is better to gradually reduce intake. |
| Sugar in Diet | While sugar has addictive qualities, it also enhances flavor and is found in many healthy foods. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This topic sparks substantial debate among health professionals. While sugar does create cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive in the traditional sense. Recognizing sugar’s role in our diets and its potential effects on our cravings provides valuable insights into managing consumption healthily. Understanding the balance and adhering to nutritional recommendations can ensure that sugar enhances our diet rather than detracts from it.