Stem cell therapy for the cornea is emerging as a groundbreaking solution for individuals suffering from severe corneal damage previously deemed untreatable. This innovative technique, which utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), involves harvesting healthy stem cells from a patient’s unaffected eye. These cells are then expanded into grafts that can be transplanted into the damaged eye, promoting corneal repair and restoration of vision. In recent clinical trials, this ocular stem cell treatment has shown remarkable effectiveness, achieving over 90 percent success in restoring the corneal surface in patients with blinding injuries. As researchers continue to explore this promising avenue, stem cell therapy stands poised to transform eye injury treatment, offering hope to countless individuals with corneal damage.
Alternative approaches to eye care are gaining traction with advancements in regenerative medicine, particularly in corneal restoration. The use of stem cell-based techniques, specifically designed to repair ocular tissues, offers an exciting new horizon for those affected by ocular pathologies. Techniques involving the cultivation of limbal epithelial cells from healthy eyes present a substantial opportunity for effective corneal damage repair. Clinical trials are paving the way for innovative therapies that may soon redefine how we approach treatment for severe eye injuries. As researchers delve deeper into ocular stem cell treatments, the potential for improved outcomes in visual rehabilitation continues to expand.
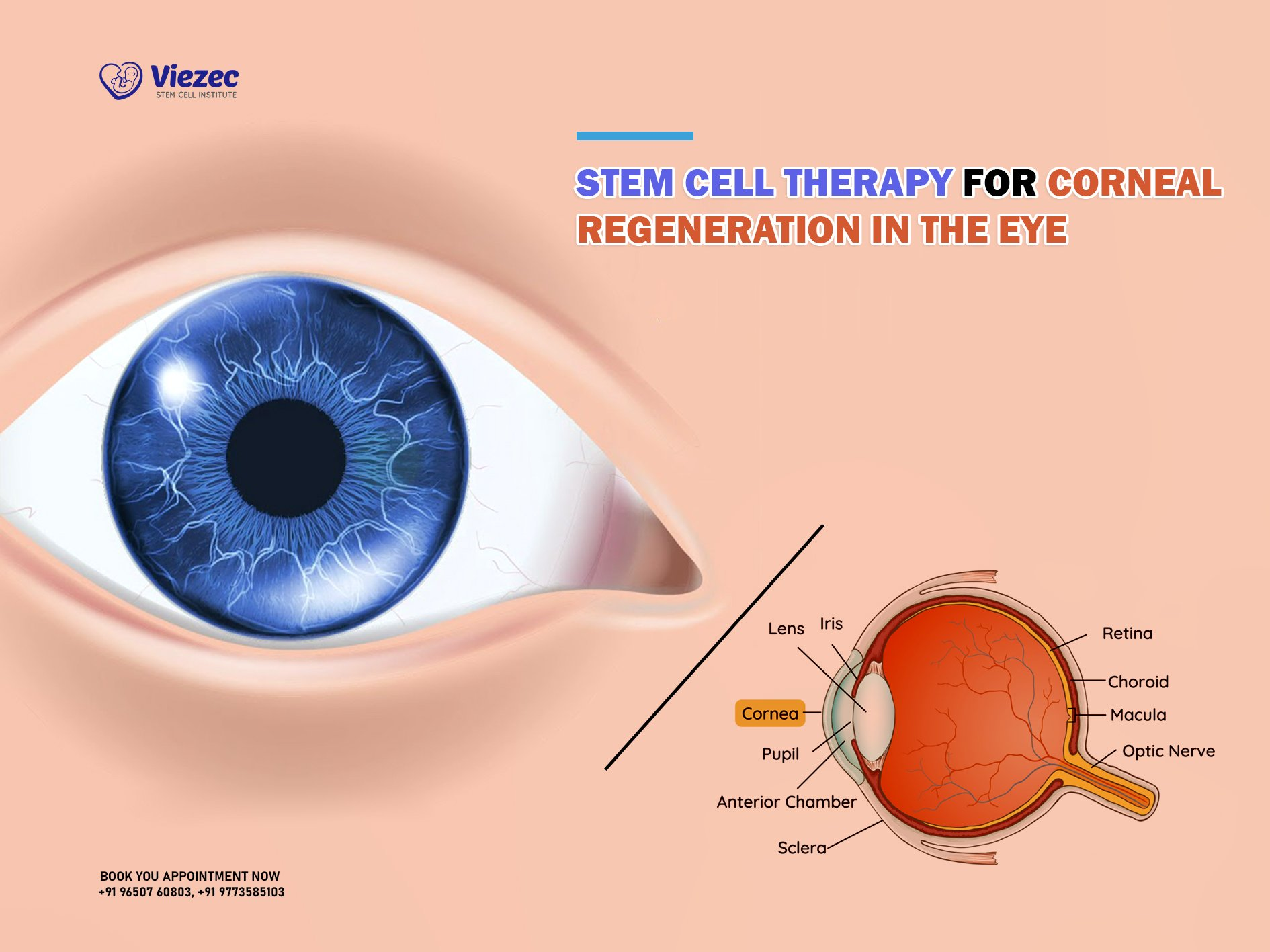
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy for Cornea Repair
Stem cell therapy for cornea repair is revolutionizing the way we approach treatment for severe ocular injuries and diseases. This method utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), which are obtained from a healthy eye and cultivated to create a tissue graft. The primary aim is to restore the clarity and function of the cornea in patients experiencing corneal damage due to trauma, chemical burns, or infections. With a dramatic success rate of over 90% observed in recent clinical trials, this innovative treatment offers new hope for many who previously faced irreversible vision loss.
One of the critical advantages of using stem cell therapy is its potential for regenerating the limbal epithelial cells that are crucial for maintaining the cornea’s surface integrity. As these cells are often depleted following significant ocular injuries, the ability to harvest and replicate them from a healthy eye provides a viable solution that complements existing treatments, such as corneal transplants. Additionally, the safety profile demonstrated in trials, with a low incidence of serious adverse effects, further establishes CALEC as a promising intervention in ocular stem cell treatment.
The Innovative Process Behind CALEC Surgery
The CALEC surgery begins with a biopsy from the patient’s healthy eye, where limbal epithelial cells are harvested. From this biopsy, these cells are meticulously cultivated in a controlled laboratory setting, which can take two to three weeks before a suitable graft is ready for implantation. This innovative process not only emphasizes the regenerative capabilities of stem cells but also showcases advancements in cell therapy manufacturing. The involvement of specialized facilities, such as the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, ensures that these grafts meet stringent quality and safety standards required for human transplantation.
Following successful cultivation, the graft is surgically transplanted into the damaged eye, where it plays a critical role in corneal damage repair. During trials, researchers observed significant improvements in the cornea’s surface condition, with a restoration rate of 50% at just three months post-surgery. This percentage increased significantly with time, reinforcing the efficacy of this ocular stem cell treatment. The careful coordination between surgical teams and cell manufacturing units has been pivotal in the successful outcomes of CALEC operations.
Clinical Trials and Their Impact on Eye Injury Treatment
Clinical trials for the CALEC procedure have marked a groundbreaking moment in treating eye injuries that were once deemed untreatable. These trials, which are the first of their kind funded by the National Eye Institute, incorporated rigorous evaluation methods and a thorough follow-up process. Over a span of 18 months, patients demonstrated remarkable positive changes in their visual acuity and quality of life. Such outcomes not only vindicate the therapeutic approach but also highlight an emerging paradigm in ocular repair strategies.
The safety and effectiveness of CALEC surgeries set a new benchmark for ocular therapies aiming to combat corneal damage. These studies serve as a beacon of hope for future research, aiming to expand the eligibility for treatment—potentially addressing cases where both eyes are affected. As further trials launch nationwide, the goal remains to validate these promising results and seek FDA approval, facilitating wider access to innovative therapies for corneal repair.
Future Directions in Ocular Stem Cell Treatments
The future of ocular stem cell treatments is bright, particularly with the ongoing advancements demonstrated through CALEC procedures. Researchers are exploring allogeneic approaches, which utilize limbal stem cells from normal cadaveric donor eyes. Such innovations could greatly increase the number of patients eligible for treatment, especially those suffering from bilateral corneal injuries. This shift towards a more inclusive model represents a significant step forward in the field of ocular regenerative medicine.
In addition, future clinical studies are expected to enhance the efficacy and safety profiles of these treatments further. Larger trial groups, randomized-control designs, and longer follow-up periods will be crucial as researchers seek to refine the CALEC process and cement its place in standard eye injury treatment protocols. Ultimately, the ongoing research intends not just to restore sight but to improve the overall quality of life for individuals affected by corneal damage.
The Role of Quality Control in Stem Cell Manufacturing
Ensuring the quality and integrity of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells is paramount in the success of CALEC therapies. Stringent quality control measures are implemented during the entire manufacturing process to ensure that the stem cells used are viable, safe, and effective for transplantation. Such measures include rigorous testing for cellular purity, proper growth conditions, and monitoring for potential contamination. Only through high-quality standards can the risks associated with the transplantation be minimized, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Furthermore, these quality control initiatives not only bolster the credibility of the clinical trial data but also pave the way for future regulatory approval. As stem cell therapy for cornea repair gains traction, maintaining a commitment to high manufacturing standards will be critical in gaining trust from both the medical community and patients. This commitment extends beyond CALEC and inspires confidence in other ocular stem cell treatments as they emerge into the clinical landscape.
Advancements in Corneal Damage Repair Techniques
With advancements in surgical techniques and regenerative medicine, the landscape of corneal damage repair continues to evolve. CALEC is at the forefront of these innovations, demonstrating that effective recovery from severe ocular injuries is possible through regenerative strategies. In contrast to traditional approaches that primarily involve corneal transplants, these novel techniques leverage a patient’s own biological materials, reducing the risk of rejection and enhancing the body’s natural healing capabilities.
As more research unfolds, we can expect to see a broader array of treatments emerging that are not only effective but also customizable based on patient-specific needs. This inclination towards personalized medicine is particularly crucial for patients with unique eye injury profiles. Emphasizing the importance of serious exploration in ocular stem cell treatments can unlock further breakthroughs in patient care and recovery pathways.
Safety Profiles of New Ocular Therapies
The safety profile of new ocular therapies, particularly stem cell treatments, is a matter of paramount concern in clinical research. In the CALEC trials, an overwhelming majority of participants experienced no serious complications, showcasing the promising safety of utilizing cultivated limbal epithelial cells. Only minor incidents were reported, which promptly resolved, underscoring that this procedure could be a viable alternative to more invasive options currently available in eye care.
This positive safety data reinforces the potential for adopting CALEC as a standard treatment for corneal damage in clinics. As additional trials are conducted and the body of evidence continues to grow, it will be vital to maintain a focus on patient safety to ensure that any new therapies introduced into practice are not only effective but also consistently safe for every patient population.
Regulatory Approval for Stem Cell Therapies
Navigating the path to regulatory approval for new stem cell therapies, including CALEC, is essential for transforming experimental treatments into widely available options for patients. The process involves intense scrutiny and comprehensive data collection, ensuring that therapies meet all safety and efficacy standards set by governing bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Once adequately established through clinical trials, these findings must be meticulously presented to facilitate a robust approval process.
Successful FDA approval would signify a tremendous milestone not only for the CALEC approach but also for the field of ocular stem cell treatments overall. It would legitimize stem cell applications in ophthalmology and potentially open doors for future innovations in this rapidly advancing field. The anticipation surrounding these upcoming trials and their outcomes reflects a collective hope for new solutions to address corneal damage effectively.
Accessibility of Ocular Stem Cell Treatments
Ensuring that ocular stem cell treatments are accessible to patients in need is critical to maximizing their impact. Currently, the CALEC procedure is still in the experimental phase and not readily available at many hospitals across the U.S. However, as trials progress and regulatory approvals are sought, efforts must be made to bridge the gap between research findings and clinical practice. This includes establishing partnerships between research institutions, regulatory bodies, and healthcare providers.
Efforts to improve accessibility should also focus on patient education, ensuring that those with severe corneal damage are aware of their treatment options. As CALEC and similar therapies expand, empowering patients through knowledge about the benefits and possibilities of these treatments will be fundamental in providing equitable healthcare solutions for ocular injuries. Facilitating access to innovative therapies is not merely about treatment but about restoring hope and vision to countless individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy for cornea damage?
Stem cell therapy for cornea damage involves the use of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) to repair the eye’s surface after injuries or diseases that deplete limbal epithelial cells, essential for maintaining corneal integrity.
How does cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) work in corneal healing?
CALEC works by taking healthy stem cells from the limbus of one eye, expanding these cells into a graft in a lab, and then transplanting the graft into the damaged eye, facilitating corneal surface restoration.
What types of eye injuries can benefit from ocular stem cell treatment?
Ocular stem cell treatment, particularly CALEC, is beneficial for various eye injuries including chemical burns, infections, and trauma that cause limbal stem cell deficiency, leading to corneal damage.
What is the success rate of stem cell therapy for cornea in clinical trials?
In clinical trials, stem cell therapy using CALEC has shown a success rate of over 90% in restoring the corneal surface in patients with severe eye damage after 12 and 18 months of follow-up.
Is stem cell therapy for cornea available in hospitals?
Currently, stem cell therapy for cornea, specifically CALEC, remains experimental and is not widely available in hospitals as it awaits further studies and FDA approval.
What are the potential side effects of stem cell therapy for corneal damage?
While CALEC therapy has shown a high safety profile, potential side effects can include mild adverse events like infections, which can often resolve quickly with proper management.
How long does it take to prepare a graft for stem cell therapy for cornea?
Preparing a graft for stem cell therapy using cultured autologous limbal epithelial cells typically takes about 2 to 3 weeks, during which the stem cells are expanded into a transplant-ready graft.
What are the next steps for research on stem cell therapy for corneal injuries?
Future research on stem cell therapy for corneal injuries involves conducting larger clinical trials with longer follow-ups to gather more data and support the quest for FDA approval.
Who can qualify for stem cell therapy for corneal damage?
Patients with unilateral corneal damage and a healthy eye from which to harvest limbal epithelial cells are currently the main candidates for stem cell therapy for cornea.
What makes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy a breakthrough for corneal damage?
The cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy is a breakthrough because it offers a potential solution for treating corneal damage that was once deemed untreatable, using patients’ own cells to promote healing.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Procedure Overview | Stem cell therapy involves removing stem cells from a healthy eye, expanding them into a graft, and transplanting it into a damaged cornea. |
| Clinical Trial Results | The trial showed CALEC was 90% effective in restoring corneal surfaces over 18 months without serious adverse events. |
| Conditions Treated | The therapy aims to treat limbal stem cell deficiency caused by injuries like chemical burns and infections. |
| Future Directions | There is hope to develop an allogeneic method using stem cells from cadaveric donors to help patients with both eyes affected. |
| Safety and Efficacy | The procedure is deemed safe, showing high success and low complication rates in participants. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy for cornea represents a groundbreaking advance in treating previously untreatable eye injuries. Developed through a clinical trial led by Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) to restore corneal surfaces effectively. The therapy demonstrated over 90% efficacy during follow-up, making it a promising solution for individuals suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency. Continued research aims to enhance accessibility and eventually gain federal approval, potentially transforming the landscape of ocular repair.