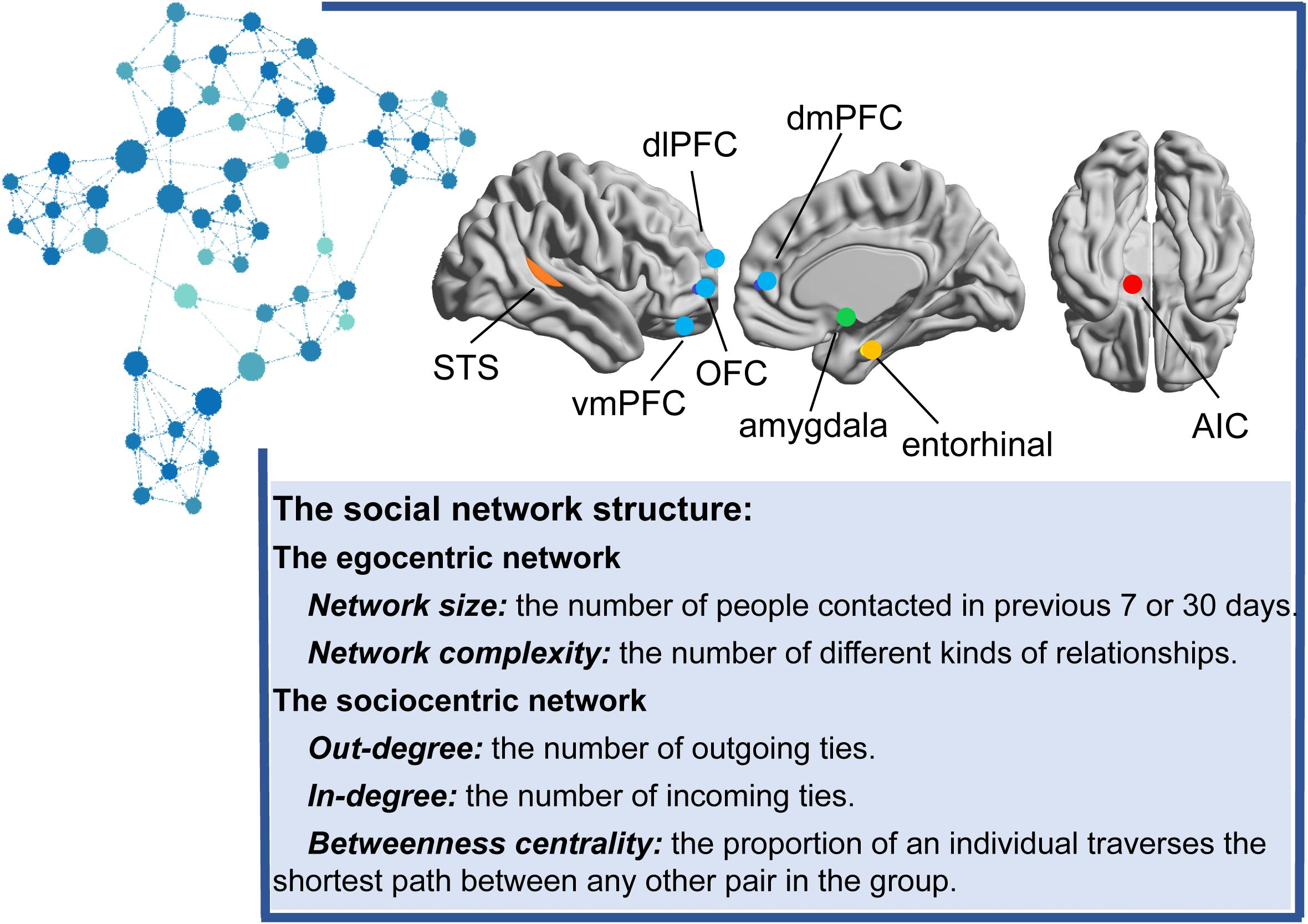
The neurological basis of social interactions plays a crucial role in our understanding of why social connections are fundamental to human well-being. Recent research has illuminated how our brains are wired for social engagement, highlighting the impact of isolation on health and mental functioning. A lack of meaningful social interactions can lead to significant mental health challenges, illuminating the importance of touch in social interactions that foster connection. The interconnectedness of social health and neurological responses underpins the essential nature of relationships in maintaining mental wellness. As science continues to unravel these intricate connections, we gain valuable insights into how fulfilling our social needs directly influences our overall health.
Exploring the brain’s role in human connectivity reveals vital insights into our social needs and behavior. The neurological underpinnings of social interactions, often referred to in studies of social connection research, show how critical these interactions are for mental balance. As we examine the effects of social isolation, it becomes evident that the absence of touch and companionship can negatively impact our overall health and mental fulfillment. Understanding these connections helps clarify why social engagement is not just beneficial but essential for mental health and well-being. By delving into the brain’s responses to social stimuli, we uncover the profound significance of human relationships and their role in fostering emotional resilience.
Understanding the Neurological Basis of Social Interactions
The human brain is a complex organ with intricate mechanisms that govern our social behaviors and interactions. Recent research, led by Ding Liu and his colleagues, has made significant strides in unraveling the neurological basis of social interactions, indicating that the pursuit of companionship is hardwired into us. This study highlights that the hypothalamus, a part of the brain traditionally associated with basic physiological needs like hunger and thirst, also plays a critical role in regulating our social urges. This revelation underlines the idea that social connection is as vital for human health as food and water, establishing it as a key area for further research in social connection studies.
Moreover, this neurological approach to understanding human interactions expands on prior social health studies that have categorized social bonds as fundamental to our well-being. With the U.S. Surgeon General’s outlook on social isolation being a public health concern, exploring the brain’s circuitry sheds light on the importance of social interactions. Researchers posit that social needs may emerge from mechanisms designed to combat discomfort, reframing our understanding of loneliness as a critical health issue rather than a mere emotional state.
The Impact of Isolation on Mental Health
The findings from the study conducted by Liu and his team delve deep into the adverse effects of isolation, particularly concerning mental health. Prolonged periods of social deprivation can lead to detrimental changes in behavior and an aversion to socializing, as reported in their experiments with mice. Interestingly, these behavioral shifts mirror those seen in human conditions such as depression and autism, wherein individuals often experience a profound disconnection from social environments. Understanding the biological mechanisms underpinning these changes can guide interventions aimed at combating isolation and its associated mental health challenges.
Mental health professionals advocate for the importance of nurturing social connections as a buffer against feelings of loneliness, which can often spiral into more significant health issues. By establishing a clearer understanding of how isolation impacts emotional and psychological states, healthcare practitioners can develop strategies that encourage social interaction. Incorporating findings from social connection research, such as the role of touch in interactions, advocates for more holistic approaches in mental health care, emphasizing the need for community-building and supportive social networks.
Importance of Touch in Social Interactions
The study by Liu further uncovers the pivotal role of touch as a significant aspect of social interaction, which has been overlooked in the digital age dominated by virtual communication. The research illustrates that physical contact, such as hugging or handshaking, activates specific neural circuits that fulfill our social needs, emphasizing touch’s biological importance in human relationships. This aligns with the existing literature on social health that underscores tactile experiences as fundamental for fostering secure attachments and emotional well-being.
As people increasingly turn to screens for social interaction, understanding the necessity of touch becomes even more relevant. The research reveals that even partial sensory inputs like sight and sound do not fully compensate for the lack of physical proximity. Thus, incorporating tactile engagement strategies in social settings could serve as a remedy for the disconnection felt in modern society. Recognizing touch’s influence on mental health and overall social connectivity can inspire new practices that emphasize meaningful physical interactions and contribute to healthier interpersonal relationships.
The Relationship Between Social Connections and Overall Health
There is growing evidence from studies exploring the relationship between social connections and overall health that underscores the idea that social interactions can positively impact long-term well-being. Research indicates that strong social networks correlate with lower risks of various health conditions, ranging from cardiovascular diseases to mental health disorders. Liu’s work reinforces that social contact does not merely enhance emotional fulfillment but is intricately linked to physical health outcomes, thereby advocating for a broader understanding of health that includes social dimensions.
Additionally, the importance of fostering social connections can lead to practical applications in public health initiatives aimed at reducing isolation. By promoting community engagement, support groups, and fostering environments that encourage socialization, healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in enhancing public well-being. The integration of social health into health policy could pave the way for addressing factors contributing to the health crisis exacerbated by isolation, bridging the gap between physical health and mental well-being.
Exploring Human Behavior Through Social Needs
The investigations into the neurological circuits governing social needs provide a unique lens to explore human behavior and motivations. This fresh perspective shifts the focus from merely enjoying social interactions to understanding the fundamental biological urges driving these behaviors, akin to hunger or thirst. By recognizing that our desire for companionship may stem from an innate need to protect ourselves from discomfort, researchers can better comprehend the complexities of human social behavior.
Consequently, this foundational knowledge can influence various fields, including psychology, sociology, and neuroscience, enriching our understanding of how social bonds are formed and maintained. Moreover, uncovering the underlying neural mechanisms could pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing social capabilities in individuals facing mental health challenges, highlighting the intersection of biology and psychology in shaping our social lives.
Implications of Findings for Therapeutic Practices
The outcomes of Liu’s study reveal essential implications for therapeutic practices, especially in developing interventions aimed at individuals dealing with social anxiety or disorders that impede social interaction. Recognizing the underlying neurological triggers that initiate a need for companionship opens up possibilities for tailored therapies that address these intrinsic drives. For example, incorporating methods that promote physical touch—such as hand-holding or hugging during therapy sessions—may enhance therapeutic rapport and assist clients in overcoming social barriers.
Additionally, the findings can inform mental health practitioners about the significance of addressing isolation in their treatment plans. Encouraging clients to build and maintain supportive social networks could transform therapeutic outcomes. By integrating insights from social connection research and understanding the longstanding benefits of social engagement, therapists can foster environments conducive to healthier social experiences and overall well-being.
The Future of Social Connection Research
As we progress into an era where social interactions increasingly take place in digital formats, the future of social connection research will be pivotal in guiding societal adaptations. The insights gained from studies like Liu’s will be crucial in understanding the shifting paradigms of human interactions. Researchers will need to delve deeper into how virtual connections can be harmonized with physical interactions to promote overall social health. New methodologies that assess both in-person and online social engagements will emerge as significant areas of study.
Furthermore, ongoing research may uncover additional dimensions of social connection, including how different cultures perceive touch or the disparity in social needs across various demographics. This expands the canvas for the intersectionality of health, sociology, and neuroscience, paving the way for more nuanced approaches to preserving social health in diverse populations. By staying attuned to these developments, we can strive towards ensuring that social needs are adequately met in a constantly evolving global landscape.
Conclusion: The Necessity of Social Interactions
In summary, the research conducted by Liu and his team has illuminated the necessity of social interactions in maintaining not only mental health but holistic well-being. By identifying the underlying neurological circuits that control social urges, healthcare providers and policymakers can better understand the implications of social health and its direct correlation with physical health outcomes. As we confront the growing challenges posed by social isolation in modern society, the critical importance of nurturing social interactions has never been more evident.
In light of these findings, it becomes imperative to promote policies that emphasize social connection as a fundamental human right. By fostering environments that encourage touch, face-to-face interactions, and meaningful relationships, we can combat the detrimental effects of isolation and improve overall health outcomes. The pursuit of happiness may very well be intertwined with the language of our brains, emphasizing that to thrive, we must connect.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social interactions and its importance for social health?
The neurological basis of social interactions is rooted in brain circuits that regulate our desire and need for companionship. Studies suggest that social connection is as essential for health as food and water, highlighting its significance for social health. Disruptions in these neural circuits can lead to social isolation, which is a major public health concern, stressing the critical link between social needs and overall mental well-being.
How do social connection research studies contribute to our understanding of mental health?
Social connection research has revealed that the need for social interactions is encoded in the brain similarly to basic human needs such as hunger. Understanding these neurological mechanisms helps researchers identify how deficits in social connections can exacerbate mental illnesses like depression and anxiety, thus contributing to more effective mental health treatments.
What impact does isolation have on health according to recent neurological studies?
Recent studies indicate that isolation can severely affect mental and physical health. The neurological research has shown that prolonged social isolation triggers changes in brain functions, leading to a decreased desire for social interactions and may increase negative feelings. This highlights the importance of maintaining social connections to mitigate health risks associated with isolation.
What is the significance of touch in social interactions and its neurological implications?
Touch plays a critical role in fulfilling social needs and is essential in social interactions. Neurological studies have shown that sensory inputs, particularly tactile experiences, are fundamental for social well-being. For example, research on mice indicates that the preference for physical touch can directly impact their social behavior, underscoring the importance of touch for human interactions too.
How can understanding the neurological basis of social needs improve our mental health strategies?
By exploring the neurological basis of social needs, mental health strategies can be developed to address the biological and psychological aspects of human behavior. This understanding can inform interventions aimed at enhancing social connections and reducing isolation, leading to improved mental health outcomes.
What are the implications of the findings on social interactions for modern society?
The findings underscore the necessity of face-to-face interactions in our increasingly digital world. As many social interactions occur online, the lack of physical touch and personal connection can lead to negative health outcomes. Recognizing this can help prioritize emotional well-being and promote healthier social practices.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Needs as Human Necessities | Social connections are essential human needs, comparable to food and shelter. |
| Research Significance | The study published in *Nature* focuses on the neurological basis of social interaction, revealing how needs for companionship are encoded in the brain. |
| Loneliness and Mental Health | Lack of social interactions is linked to mental illness, emphasizing the need for a deeper understanding of our social instincts. |
| Research Methodology | Mice were isolated for different durations to study their responses to social deprivation and how it affects their desire for interaction. |
| Touch as a Social Stimulus | Experiments showed that tactile interactions are crucial for fulfilling social needs, suggesting similar significance in humans. |
| Implications of Findings | Understanding the biological and psychological roots of social behavior is necessary for appreciating its impact on mental health. |
Summary
The neurological basis of social interactions reveals that social connection is as vital to human well-being as food or shelter. Recent studies illustrate how our brains encode the instinctive need for companionship and how isolation can lead to detrimental mental health effects. Understanding these biological roots not only underscores the importance of social bonds but also offers insights into improving mental wellness and interpersonal relations in our increasingly digital age.