Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer has emerged as a critical focus in understanding liver disease progression, especially with regards to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of this cancer. Recent studies highlight how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can initiate a cascade of liver damage, culminating in cancer. As bile acids play a crucial role in fat digestion and act as metabolic regulators, their imbalance can lead to serious health issues, including enhanced tumor growth. Researchers are delving into innovative liver cancer treatment strategies, with a particular emphasis on YAP FXR signaling, which offers insights into potential therapeutic interventions. This growing body of knowledge underscores the necessity of addressing bile acid dysregulation to combat liver-related diseases effectively.
The relationship between bile acid dysregulation and hepatic malignancies has become a vibrant area of research, thereby shedding light on new avenues for treating liver ailments. Often described in the context of liver health, this imbalance can severely impact bile production and digestion, ultimately leading to severe conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the complex interplay between bile acids and metabolic pathways, including critical roles played by the Hippo/YAP signaling axis, offers hope for novel treatment options for liver cancer and other liver diseases. Ongoing investigations into bile acid homeostasis are crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and enhancing our comprehension of liver disease mechanisms. As we explore alternative therapies, unraveling the nuances of bile acid functionality and their impact on liver cell signaling remains paramount.
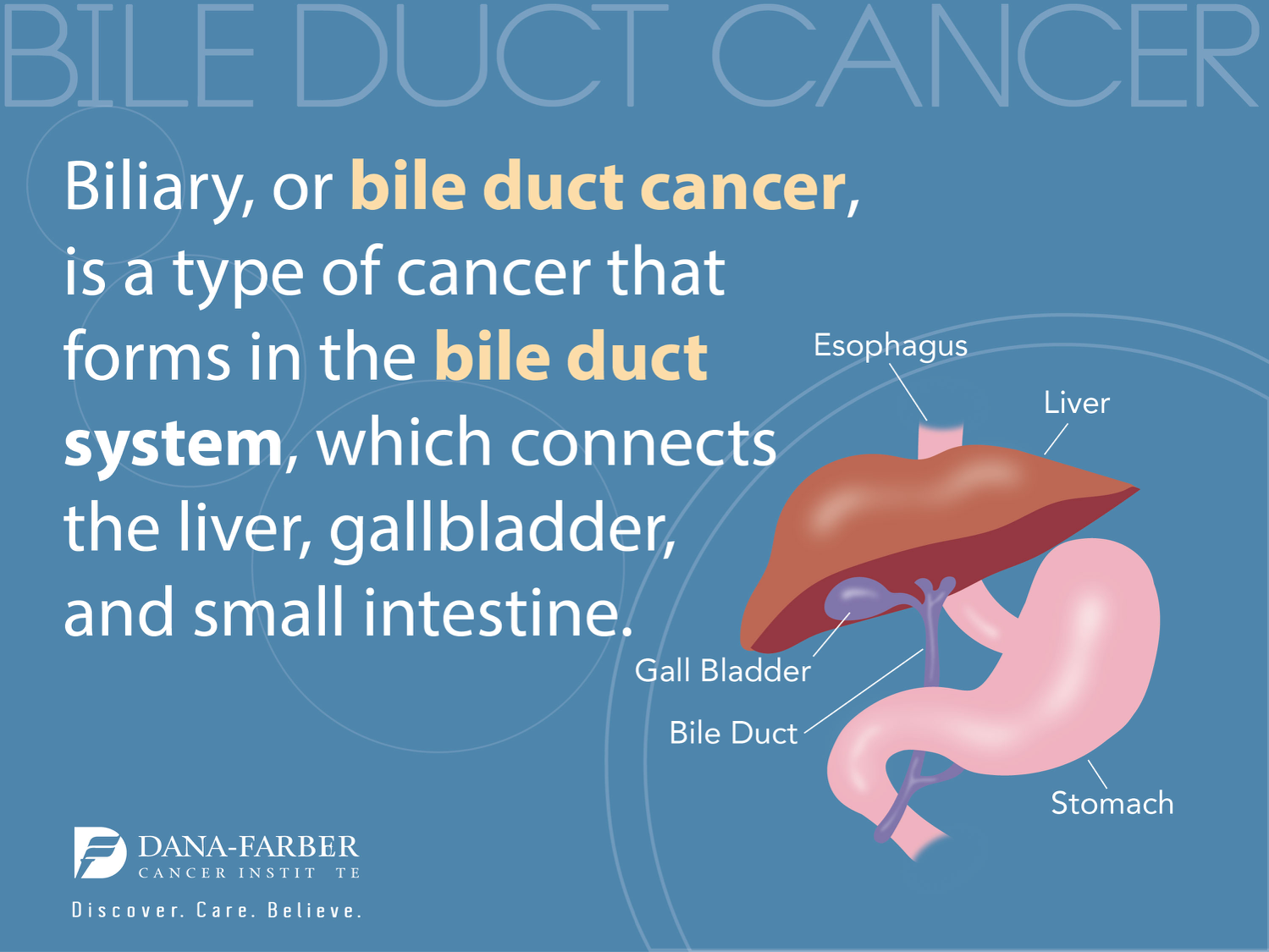
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance plays a critical role in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, which are produced by the liver, not only aid in fat digestion but also play a significant role in regulating various metabolic processes in the body. A disruption in the balance of these bile acids can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and ultimately cancerous changes in liver cells. Research has shown that the signaling pathways involved in bile acid metabolism, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway, are pivotal in maintaining hepatic health.
Recent studies highlight how alterations in bile acid metabolism can initiate a cascade of events leading to liver disease progression. The key molecular switch identified in the research demonstrates that when the YAP protein inhibits FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), the liver cannot effectively regulate bile acid levels. This overproduction causes toxic buildup, promoting inflammation and fibrotic changes, which are precursors to liver cancer. Understanding this mechanism opens potential avenues for targeted liver cancer treatment that aim to restore normal bile acid function.
The Role of YAP FXR Signaling in Liver Disease
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is integral to cell growth and survival, particularly in the context of liver disease. YAP functions as a transcriptional regulator that, in certain conditions, can promote tumor formation. In the context of bile acid metabolism, a notable role of YAP has been to repress the activity of FXR, which is essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When YAP is activated, it can lead to an excess of bile acids, contributing significantly to liver injury and advancing the progression of diseases like HCC.
Modulating YAP FXR signaling presents a promising therapeutic strategy for addressing bile imbalance and its consequences. Research has shown that enhancing FXR function or decreasing YAP activity can reverse bile acid overload, thereby mitigating liver damage. This opens up exciting possibilities for pharmacological interventions that could target this pathway, providing a more effective approach to liver cancer treatment and management of liver diseases. Understanding these signaling interactions is critical, as it can lead to innovative strategies that address the metabolic disruptions associated with liver cancer.
Innovative Approaches to Liver Cancer Treatment
Recent advancements in understanding bile acid metabolism and its link to liver cancer have spurred innovative approaches in treatment strategies. By targeting the molecular switches identified in recent studies, researchers are exploring new pharmacological options that could stimulate FXR and restore normal bile acid function. These treatments aim to break the cycle of bile acid buildup that leads to liver injury and carcinogenesis, offering hope for better outcomes in patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma.
In experimental models, researchers have shown that activating FXR, inhibiting YAP’s repressing functions, or enhancing bile acid excretion can significantly reduce liver damage and slow cancer progression. Such targeted therapies could revolutionize how we treat liver diseases and reduce the incidence of complications associated with liver cancer. Continued research in this field is essential as it uncovers more about the intricate relationship between bile imbalance, liver cancer, and the potential pathways we can exploit for effective treatment.
Bile Acid Metabolism as a Therapeutic Target
The role of bile acid metabolism in liver health cannot be overstated. Given its significant effects on liver function and its correlation with liver cancer, therapeutic strategies that focus on restoring bile homeostasis are gaining traction. The critical insights from recent research into YAP and FXR signaling underscore the potential for targeting these pathways to correct metabolic imbalances. Adjusting bile acid levels may not only prevent liver damage but could also reverse the cancerous transformations in hepatocytes.
As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver cancer treatments, there is optimism for developing innovative drugs that harness these findings. With better understanding and tools, healthcare providers may one day offer personalized treatment plans that effectively target bile acid imbalances and reduce the risk of liver disease progression. This approach reflects a significant shift in how liver-related conditions, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, are viewed and treated in modern medicine.
Linking Bile Imbalance to Broader Liver Diseases
Bile imbalance is not only associated with liver cancer but also with a range of other liver diseases. Conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and bile acid malabsorption can produce similar outcomes, including inflammation and fibrosis. By understanding the role of bile acids and their metabolic pathways, researchers can develop comprehensive treatment modalities that address multiple aspects of liver health. This broader view is critical as it encompasses various liver diseases and the underlying mechanisms that may contribute to their development.
Addressing bile imbalance may provide preventive measures against liver cancer and other disorders. By restoring normal bile acid metabolism through targeted therapies that modulate FXR signaling or YAP activity, healthcare professionals could not only treat existing liver conditions but also prevent the onset of future complications. This represents a significant advancement in the fight against liver diseases, showcasing how integrated research can lead to holistic treatment approaches.
The Future of Liver Cancer Research
The future of liver cancer research lies in further understanding the molecular mechanisms that link bile imbalance to cancer progression. As studies continue to shed light on the roles of YAP and FXR in bile acid metabolism, there is a growing impetus to translate these findings into clinical practice. Innovations in genetic and genomic methodologies will enable researchers to explore new therapeutic targets, leading to breakthroughs that can change the treatment landscape for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Additionally, as more data is gathered regarding the effects of bile acid signaling on liver disease progression, researchers will be better equipped to address the increasing prevalence of liver cancer worldwide. Collaboration across various disciplines will fuel advancements in liver cancer treatments, emphasizing the importance of a multifaceted approach to tackling this global health challenge. Overall, the prospects for developing effective interventions based on bile acid metabolism and liver signaling are promising.
Impact of Bile Acid Excretion on Liver Health
Bile acid excretion is key to preventing bile acid overproduction and its associated liver damage. The liver’s ability to excrete bile acids effectively helps to balance levels and mitigate the risk of inflammation and fibrosis. Research indicates that enhancing the expression of bile acid export proteins can be a viable strategy for improving liver health and reducing the burden of liver cancer. This has significant implications, as it connects metabolic health with cancer prevention.
Promoting bile acid excretion through pharmacological agents or dietary interventions could become a cornerstone of liver disease management. Future studies may focus on identifying the most effective compounds that amplify bile acid export while reducing the toxic effects of bile acid accumulation. This proactive approach to liver health suggests a holistic model for preventing disease progression, underscoring the importance of integrated therapies in liver cancer treatments.
Integrative Strategies for Managing Liver Disease
Managing liver diseases demands a multifaceted approach that addresses the complex interplay between bile acid metabolism, cell signaling, and nutritional factors. Integrative strategies that consider dietary modifications, pharmacotherapy, and lifestyle interventions can help combat the onset and progression of liver disease, including hepatocellular carcinoma. In particular, an emphasis on restoring bile acid homeostasis can be a powerful means of improving liver function and reducing cancer risk.
Healthcare providers may see improved patient outcomes by combining different treatment modalities that focus on bile health and metabolic control. Such integrative approaches can leverage findings from molecular research to tailor interventions that target specific pathways involved in liver disease progression. This strategy not only enhances treatment efficacy but also empowers patients to engage in their health journey, advocating for proactive measures to maintain optimal liver function.
The Link Between Liver Disease Progression and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in the progression of liver diseases, influencing bile acid metabolism and overall liver function. Diets that provide adequate nutrients and limit toxic substances can help maintain a healthy liver environment. Research suggests that specific dietary patterns can enhance bile acid secretion and reduce the risk of liver injury, indicating that nutritional interventions may be an effective strategy in preventing liver cancer.
Additionally, addressing the dietary habits of individuals at risk for liver disease could significantly impact public health. Understanding the connection between nutrition, bile imbalance, and liver cancer risk can lead to evidence-based dietary guidelines tailored to protect liver health. Fostering awareness of the role of nutrition in liver disease management encourages a proactive approach to preventing hepatocellular carcinoma and related disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is crucial in the context of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The disruption of bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which may progress to cancer. Studies indicate that certain bile acids can promote tumor formation through pathways like YAP and FXR, highlighting the importance of bile acid regulation in liver cancer treatment.
How does bile acid metabolism influence liver cancer treatment?
Bile acid metabolism plays a significant role in liver cancer treatment as it impacts the progression of liver diseases. The regulation of bile acids through molecular pathways like Hippo/YAP can affect liver inflammation and fibrosis, leading to HCC. Enhancing FXR activity, a critical bile acid sensor, could provide new therapeutic strategies for managing liver cancer.
What role does the YAP FXR signaling pathway play in liver cancer?
The YAP FXR signaling pathway is central in regulating bile acid metabolism and consequently liver cancer. YAP, when activated, inhibits the function of FXR, leading to an excess of bile acids that can damage the liver and promote HCC. Targeting this pathway presents potential therapeutic options for liver cancer treatment by restoring bile acid homeostasis.
Can bile acid accumulation lead to liver disease progression?
Yes, the accumulation of bile acids due to impaired metabolism can lead to liver disease progression. Excess bile acids can cause liver inflammation and fibrosis, both of which are critical factors in the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding this progression is essential for developing effective liver cancer treatments.
What innovative treatments target bile imbalance in liver cancer?
Innovative treatments targeting bile imbalance in liver cancer involve enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion. Recent research indicates that activating FXR or inhibiting YAP’s repressor function can reduce liver damage and slow cancer progression, potentially leading to new pharmacological solutions for liver cancer treatment.
How do bile acids function beyond digestion concerning liver cancer?
Beyond aiding in digestion, bile acids function as hormone-like molecules that regulate metabolic processes. In the context of liver cancer, bile acids are involved in signaling pathways that influence liver function. Dysregulation of these bile acids can lead to disease processes that culminate in hepatocellular carcinoma, making their regulation critical for both liver health and cancer treatment.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance Causes Liver Cancer | Research shows that an imbalance of bile acids can lead to liver diseases, particularly HCC, the most common liver cancer. |
| Role of YAP in Bile Acid Metabolism | YAP, a protein studied for its role in cancer, inhibits FXR, which is vital for maintaining bile acid balance. |
| Potential Treatment Strategies | Enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion could block the damaging effects of bile acid overproduction. |
| Experimental Findings | Activating FXR, inhibiting YAP’s function, or increasing bile acid export proteins can reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Support | The study was supported by NIH and National Cancer Institute, highlighting its significant scientific backing. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a critical concern in hepatology, as recent research establishes a clear link between the overproduction of bile acids and the onset of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The study not only identified a key regulator in bile acid metabolism but also opens new avenues for pharmacological treatments aimed at restoring balance in bile acids as a potential approach to combat liver cancer.